A histogram is the best way to visualize the frequency distribution of a dataset by splitting it into small equal-sized intervals called bins. The Numpy histogram function is similar to the hist() function of matplotlib library, the only difference is that the Numpy histogram gives the numerical representation of the dataset while the hist() gives graphical representation of the dataset.
Creating Numpy Histogram
Numpy has a built-in numpy.histogram() function which represents the frequency of data distribution in the graphical form. The rectangles having equal horizontal size corresponds to class interval called bin and variable height corresponding to the frequency.
Syntax:
numpy.histogram(data, bins=10, range=None, normed=None, weights=None, density=None)
Import libraries import numpy as np # Creating dataset a = np.random.randint(100, size =(50)) # Creating histogram np.histogram(a, bins = [0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]) hist, bins = np.histogram(a, bins = [0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]) # printing histogram print() print (hist) print (bins) print()
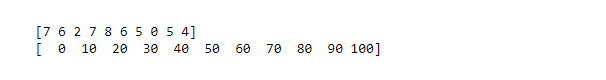
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/numpy-histogram-method-in-python/
